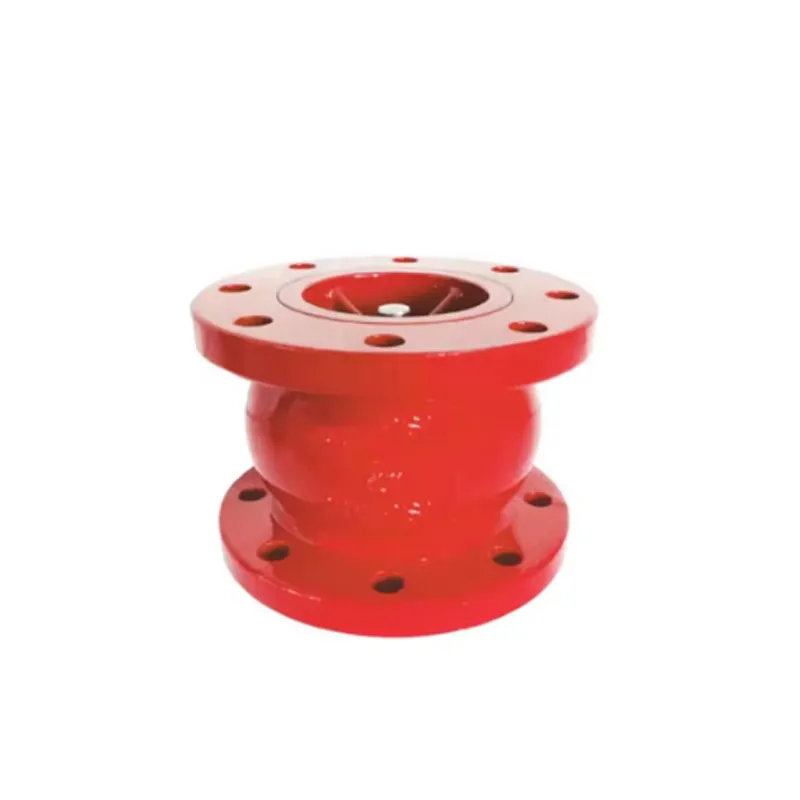
Silent Check Valve
Silent Check Valve Definition and Components
A Silent Check Valve, also known as a Non-Slam Check Valve, is a specialized type of automatic check valve designed to prevent reverse flow without the disc violently slamming onto the seat. It achieves this through an internal spring mechanism that closes the disc just before the flow reaches zero velocity, eliminating the water hammer shock and noise associated with conventional swing check valves.
Fire Check Valve Key Terminology:
- Non-Slam / Silent:The defining feature. It prevents the hydraulic shock (water hammer) caused by rapid disc closure in traditional check valves.
- Spring-Assisted Closure:An internal spring works with the forward flow to close the disc progressively as flow slows, not after it reverses.
- In-line Design:Typically has a more compact, piston-like or center-guided disc assembly compared to the long-lever arm of a swing check.
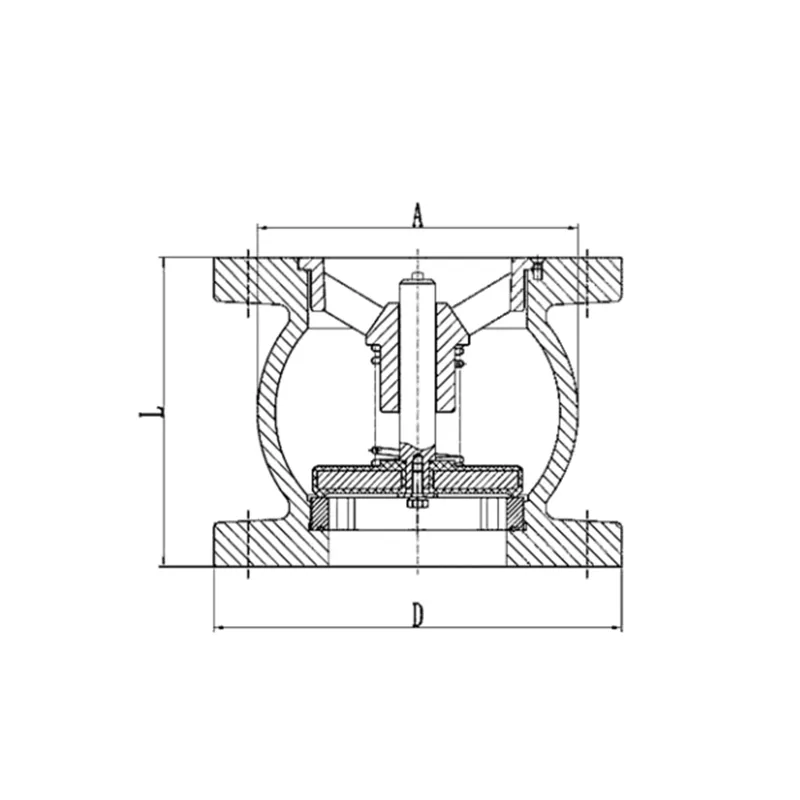
Main Parts:
- Valve Body: Housing for internal components; comes in wafer, lug, flanged, or grooved ends.
- Disc/Piston: The closure member, often guided by a stem or ribs within the body to move in a linear or slightly angled path.
- Spring: The critical component that provides the closing force. Its strength is calibrated based on pressure and flow conditions.
- Guide System: Bushings, ribs, or a central guide to keep the disc aligned and prevent wobbling.
- Seat: Resilient (rubber) or metal seat that the disc seals against.
- Retainer/Cover: Secures the internal assembly.
Role, Characteristics, and Application Scenarios of Silent Check Valve in Pipelines
Functions:
- Backflow Prevention with Zero Slam:Primary function is to prevent reverse flow while eliminating water hammer.
- System Protection:Protects pipelines, pumps, and sensitive instruments from damaging pressure surges.
- Flow Direction Control:Ensures unidirectional flow in systems with frequent start/stop cycles.
Operational Features:
- Progressive Spring-Assisted Closure:Closes smoothly before flow reversal, making it "silent."
- Vertical & Horizontal Installation:Can be installed in any orientation due to the spring force, unlike swing checks that require horizontal mounting.
- Higher Cracking Pressure:Requires a specific minimum upstream pressure to open (to overcome the spring), which can prevent unwanted opening in complex systems.
- Reduced Disc Travel:Shorter stroke than swing checks, leading to faster, more controlled closure.
- Higher Pressure Drop:The spring and guided design create more flow resistance than a full-bore swing check.
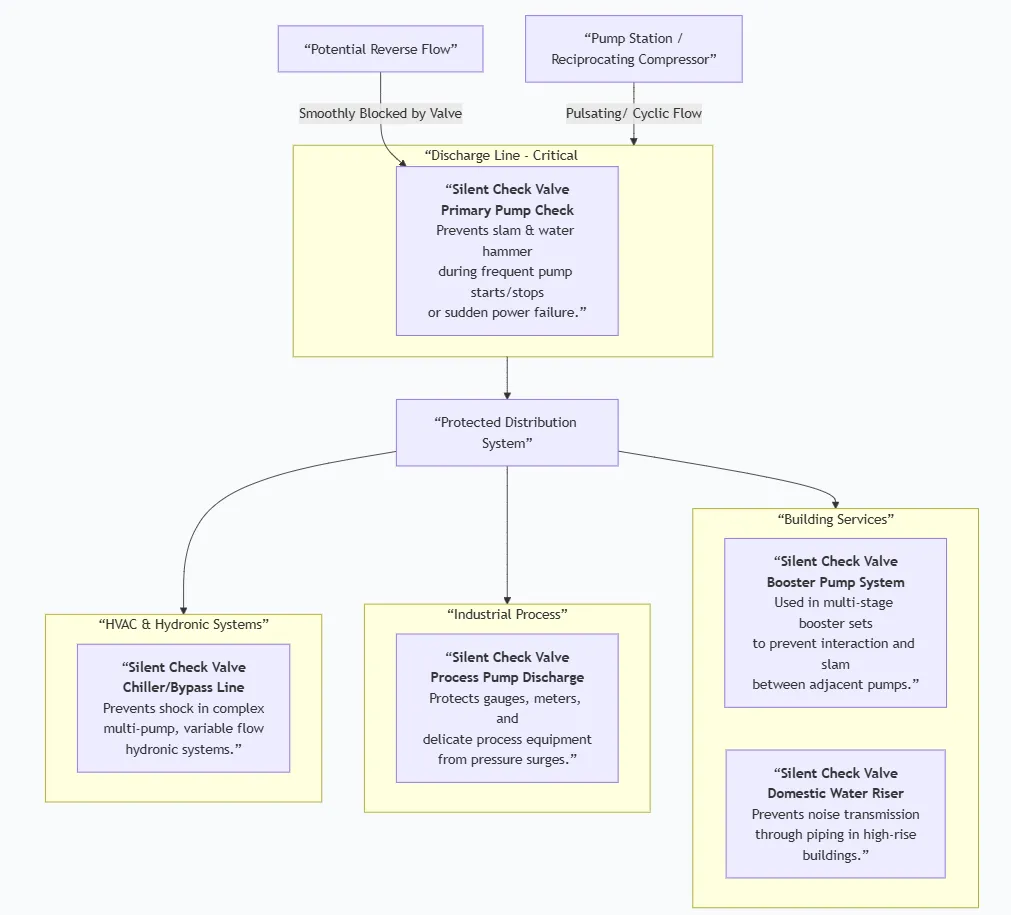
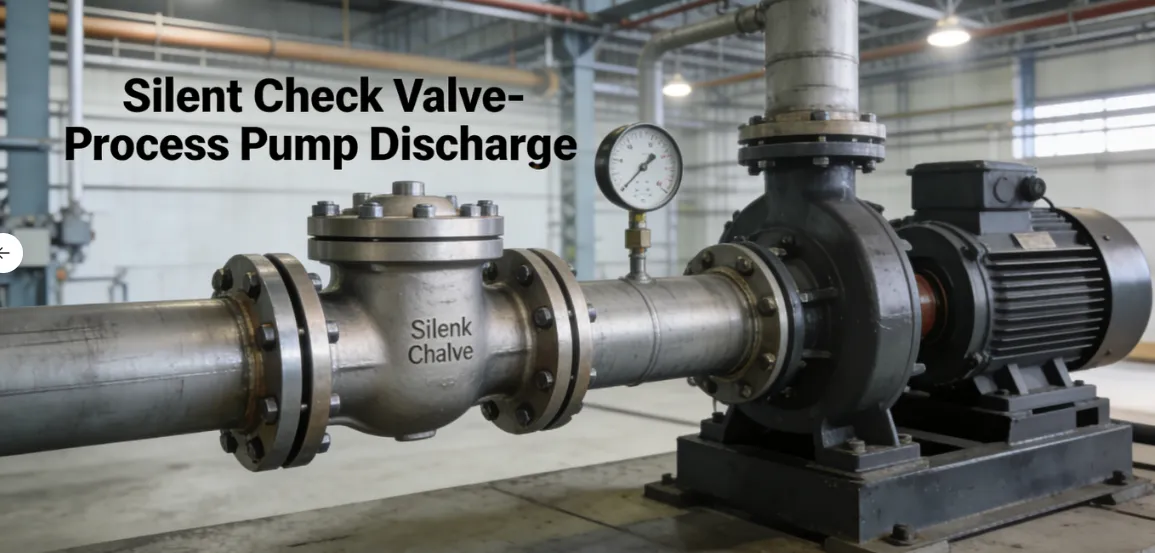
Fire Fighting Valve Primary Usage Scenarios:
Used in systems where pump cycling, rapid valve closure, or fast-flow reversal would cause problematic water hammer with a standard check valve.
Scenario Diagram:
Silent Check Valve Standards: Materials, Design, and Connections
| Standard Type | Primary Standard(s) | Purpose & Key Specifications |
| Design & Dimensions | API 594 / API 6D | API 594 is common for wafer/lug check valves. API 6D is stringent for pipeline and industrial application silent checks, often specifying spring characteristics and non-slam performance. |
| Connection Standards | ASME B16.5 (Flanged) | Defines end connections. Silent checks are commonly wafer-style but also come in flanged and grooved. |
| ASME B16.47 (Large Flanged) | ||
| ANSI/AWWA C606 (Grooved) | ||
| ISO 5752 (Wafer Face-to-Face) | ||
| Material Standards | ASTM A216 WCB (Carbon Steel) | Body and trim materials. Spring is typically ASTM A313 Stainless Steel. |
| ASTM A351 CF8/CF8M (Stainless Steel) | ||
| ASTM A536 (Ductile Iron) | ||
| ASTM B584 (Bronze) | ||
| Spring & Performance | Manufacturer's Specifications | Critical. Spring force (cracking pressure) and closing speed are often custom-engineered based on flow conditions. There is no single universal standard for "silent" performance—it is a functional characteristic validated by vendor testing. |
| Testing | API 598 / ISO 5208 | Standard shell and seat pressure tests. Non-slam performance is typically verified by functional test or customer witness test, not by a standard pressure test. |
How to Select Silent Check Valve
Step 1: Define Rigorous Performance Specifications
Purchasing a silent check valve is an engineering selection, not just a commodity buy.
- System Data is Crucial:Provide Flow Rate (min/max), Pressure (upstream/downstream), Fluid Properties, and Pipe Size.
- Required Performance:Specify "Non-slam" or "Silent" operation. Define the maximum allowable pressure surge upon closure if known.
- Cracking Pressure:Specify the required cracking pressure (the upstream pressure at which the valve starts to open). This is determined by the spring.
- Connection & Materials:As with any valve: end type, body/disc/seat material, and pressure class.
- Standard Reference:Specify design to API 6D for critical service, as it has more rigorous requirements for check valves.
Step 2: Engage with Technical Suppliers
- Source from manufacturers with proven expertise in fluid dynamics and silent check valve engineering.
- Require a Valve Sizing/Selection Sheet.Reputable manufacturers will provide calculations showing selected spring, expected closing time, and predicted surge pressure.
- Request detailed CAD drawings and a detailed cut sheet showing internal construction.
- For critical applications, request reference projects or performance test data.
Step 3: Validation and Order
- Consider a Factory Acceptance Test (FAT)to witness the valve's functional operation on a test loop simulating your conditions.
- Ensure the purchase order includes reference to the approved sizing sheet and performance requirements.
Pre-Shipment Inspection for Export Silent Check Valve and Key Considerations
Inspection Checklist:
| Category | Check Point | Acceptance Criteria |
| Documentation | 1. Valve Selection Data Sheet | Must be provided, showing selected spring and calculated performance. |
| 2. Material Certificates | MTRs for body, disc, spring (ASTM A313), and seat. | |
| 3. Pressure Test Certificate | Standard API 598 shell/seat test. | |
| Physical/Functional | 4. Spring Action Test | CRITICAL: With valve horizontal, the disc should move smoothly with finger pressure and return firmly via spring force. No sticking. |
| 5. Guide System Inspection | Disc must move axially without binding or lateral play. | |
| 6. Marking & Flow Arrow | Clear permanent marking, including flow direction. | |
| 7. Spring Identification | Verify spring marking/color code matches the selection sheet. | |
| Packaging | 8. Disc Securement | The disc must be blocked in the CLOSED position with a shipping restraint to prevent spring fatigue from constant compression during transit. |
| 9. End Protection | Flange faces or grooves must be protected. |
Check Valve Fire Sprinkler System Key Precautions for Export:
- Spring Protection is Paramount:The valve must be shipped with the shipping restraint installed to keep the spring compressed. This is a small pin, clip, or bracket specified by the manufacturer. It must not be removed until the valve is installed. Document this clearly.
- Orientation Marking:Mark the crate with "Internal Spring - Handle with Care" and the required installation orientation if any.
- Moisture Exclusion:Use desiccant bags and ensure packaging is watertight to prevent corrosion of the spring and guide mechanism.
- Documentation Pack:Include the Valve Selection Sheet, installation manual (with warning about the shipping restraint), and test certificates in a waterproof pouch inside the crate.
Silent Check Valve Size Chart
.png)
.png)