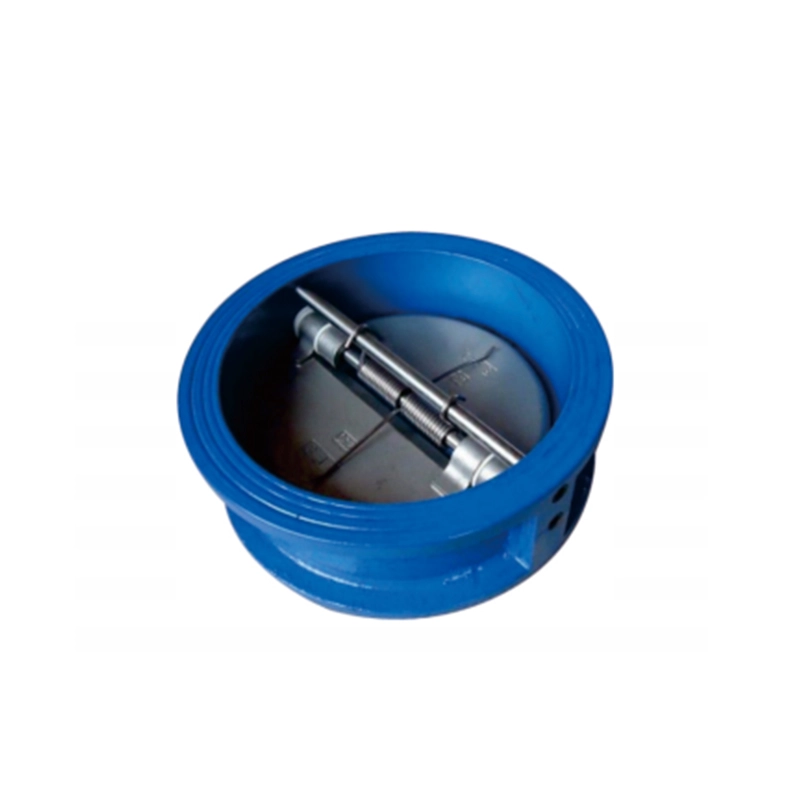
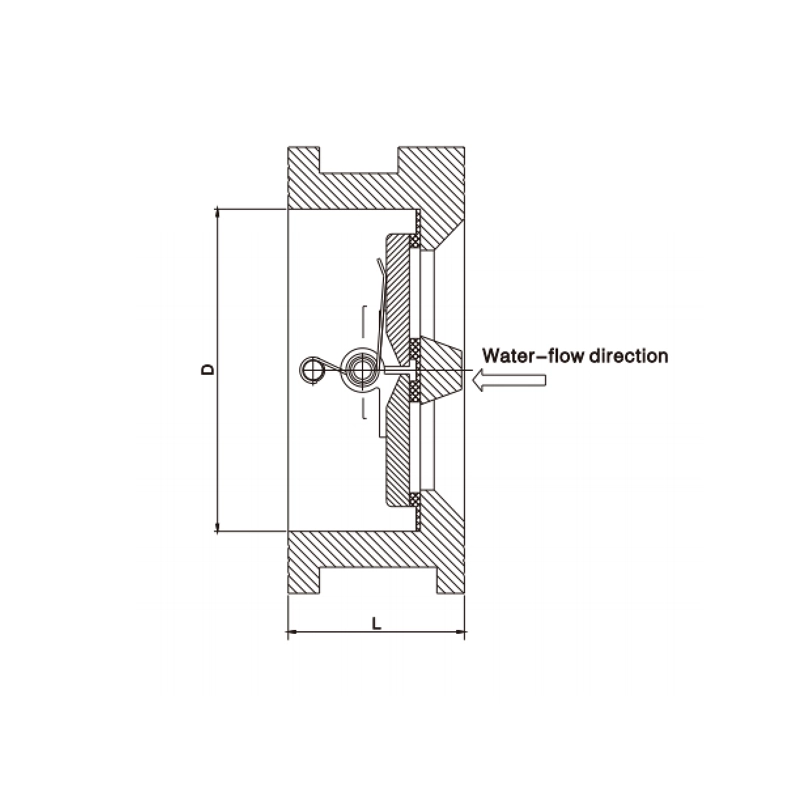
Dual Plate Check Valve
Dual Plate Check Valve Definition and Components
What is a H76X/H/W Valve?
The H76X/H/W series designates a Dual Plate (or Dual Disc) Wafer Check Valve. 'H' is the code for check valve, '7' indicates a wafer-style connection, and '6' represents the dual plate design. The suffix denotes the seat material: X for rubber/resilient, H for metal/alloy, and W for a body material (often indicating a different alloy like nickel-plated).
It is a compact, lightweight non-return valve. Two spring-loaded, hinged plates (discs) open with forward flow and slam shut to prevent backflow when flow stops or reverses.
Dual Plate Check Valve Main Parts:
- Valve Body: A short, ring-like housing, typically wafer-style with no flanges. Made from cast iron, carbon steel, or stainless steel.
- Two Plates (Discs): The two half-circle closing elements. They are connected by a hinge pin and rotate independently.
- Hinge Pin & Bushings: The central shaft on which the plates pivot. Bushings reduce wear.
- Torsion Spring(s): A critical component that provides the closing force, ensuring quick, positive closure before reverse flow begins.
- Seat: The sealing surface. This can be a resilient ring (rubber/EPDM for H76X), a metal surface integrated into the body (for H76H), or a coated surface.
- Body Seal Rings (Optional): Rubber or graphite rings on the face of the wafer body to seal against pipeline flanges.
Role, Characteristics, and Application Scenarios of Dual Plate Check Valve in Pipelines
Water Check Valve Pipeline Functions:
- Automatic Backflow Prevention: Its sole function is to automatically allow flow in one direction and prevent (check) reverse flow. It protects pumps, compressors, and other equipment.
- Water Hammer Mitigation: Rapid closure helps minimize the pressure surge associated with reverse flow.
Operational Features:
- Compact & Lightweight: Its wafer design installs between pipeline flanges, saving significant space and weight compared to swing check valves.
- Fast Closure: The spring-assisted action provides quick, positive closing, reducing slam and reverse flow velocity.
- Low Pressure Drop: The streamlined design and full-port opening offer minimal flow resistance.
- Limited Repairbility: Most are maintenance-free units; worn seats or springs often require complete valve replacement.
Water Valves Application Scenarios:
- Ideal for horizontal lines in systems requiring reliable, space-saving backflow prevention.
- Pump Discharge: The most common application, protecting pumps from reverse rotation when stopped.
- Process & Cooling Water Systems: In industrial plants and HVAC systems.
- Compressed Air/Gas Lines: Preventing backflow in instrument air systems.
- General Service Lines: Where space and weight are constraints.
Scenario Diagram (Text Description):
In a municipal water booster pump station, a horizontal centrifugal pump discharges into a rising main. A Dual Plate Check Valve (H76X with EPDM seat) is installed directly downstream of the pump, between the discharge flange and the pipeline flange. When the pump runs, water pressure pushes the two plates open against the spring force, allowing flow. If the pump trips, flow immediately decelerates. The springs instantly force the two plates closed, preventing the column of water in the rising main from flowing backwards and spinning the pump rotor in reverse, which could cause damage. Its compact wafer design fits perfectly in the cramped discharge piping of the pump skid.
Dual Plate Check Valve Standards: Materials, Design, and Connections
Material Standards:
- Body: Cast Iron (ASTM A126), Ductile Iron (ASTM A536), Carbon Steel (ASTM A216 WCB), Stainless Steel (A351 CF8).
- Plates/Discs: Typically same as body, often with rubber coating (X) or hard-facing (H).
- Spring: Stainless Steel (302/316).
- Hinge Pin: Stainless Steel.
Design Standards:
- API 594: Check Valves: Flanged, Lug, Wafer, and Butt-welding. This is the key API standard.
- API 6D: Pipeline Valves.
- ASME B16.34: Pressure-Temperature Ratings.
- MSS SP-71: Cast Iron Dual Plate Check Valves.
Connection Standards:
- Wafer Design: The valve fits between ANSI/ASME B16.5 or EN 1092-1 flanges. It uses the pipeline's bolts.
- Face-to-Face: Very short, per API 594 or manufacturer's standard.
How to Select Dual Plate Check Valve
Key Steps:
Define the Primary Purpose: Specify it's for spring-assisted, rapid closure to prevent slam and protect rotating equipment.
Select Critical Specifications
- Seat Type: H76X (Resilient) for bubble-tight shut-off in water. H76H (Metal) for higher temperatures, steam, or where rubber is incompatible.
- Spring Strength: Specify "Standard," "Light," or "Heavy" spring based on the system's flow velocity and required closing speed. Manufacturer selection charts are essential.
- Installation Orientation: Most are for horizontal pipes only. Confirm if vertical installation is needed (requires a special design).
- Verify Compatibility: Ensure the wafer thickness and bolt hole pattern match your existing pipeline flanges (ANSI vs. DIN).
- Focus on Spring Quality: Since spring failure is a common mode, inquire about spring material, corrosion protection, and testing.
Pre-Shipment Inspection for Export Dual Plate Check Valve and Key Considerations
Inspection Checklist:
- Functional Flow Test (Most Important): The valve should be tested for free movement. With the valve held horizontally, plates should swing open freely and snap closed crisply via spring action. There should be no sticking or binding.
- Dimensional Check: Verify overall thickness, diameter, and bolt hole alignment with a template.
- Pressure Test: A shell test (body) is standard. A seat test with air or water is performed to check for leakage, with acceptable rates based on seat type (zero for resilient, a drip rate for metal).
- Material Check: Verify body material stamping against the order.
Export Precautions:
- Protect the Sealing Faces: The two wafer faces are critical. Fit them with sturdy, flat cardboard or plastic covers taped securely, not bolted.
- Immobilize the Plates: Use foam blocks or straps to hold the plates in the fully closed position during transit. This prevents the hinge pins and plates from flapping and causing damage.
- Protect from Rust: For carbon steel valves, apply a light, removable rust preventative. For stainless steel, ensure surfaces are clean and dry.
- Pack Securely: These are relatively light but can be damaged by impact. Use a sturdy cardboard box or wooden crate with sufficient internal cushioning. Mark with "WAFFER VALVE - PROTECT FLANGE FACES."
Dual Plate Check Valve Main performance parameters
| Size | 40~600 | mm | ||
| Pressure | 1.0 | 1.6 | 2.5 | MPa |
| Shell test | 1.5 | 2.4 | 3.75 | |
| Sealing test | 1.1 | 1.76 | 2.75 | |
| Hermetic seal test | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | |
| Suitable temperature | <100 | °c | ||
| Suitable medium | Water | |||
Dual Plate Check Valve Main part materials
| Model | Body | Disc | Stem | Spring | Seal ring | Suitable temperature |
| H76X | Cast iron | Cast iron | Stainless steel | Stainless steel | Rubber | <100℃ |
| H76H | Cast steel | Cast steel | Stainless steel | Stainless steel | Alloy steel | 425℃ |
| H76W | Stainless steel | Stainless steel | Stainless steel | Stainless steel | Stainless steel | 425℃ |
Dual Plate Check Valve Main dimensions(mm)
| DN(mm) | 40 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 |
| L | 43 | 43 | 46 | 64 | 64 | 70 | 76 | 89 | 114 | 114 | 127 | 140 | 152 | 152 | 178 |
| D | 55 | 65 | 82 | 95 | 118 | 146 | 171 | 255 | 266 | 312 | 362 | 412 | 452 | 507 | 626 |
Note:1. Other specifications and flange standards are available upon request.
- Design and specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
.png)
.png)