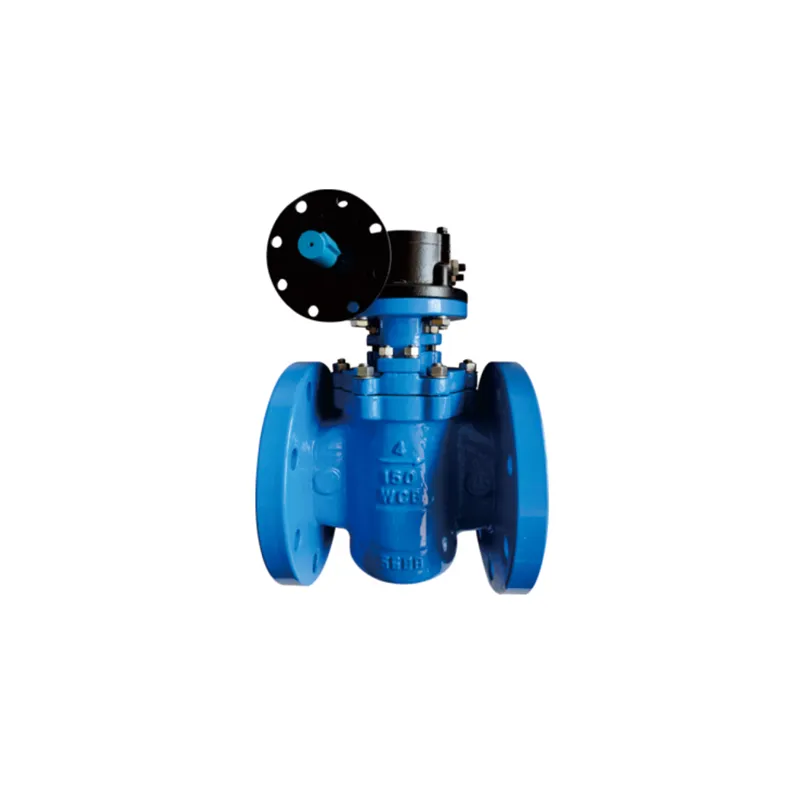
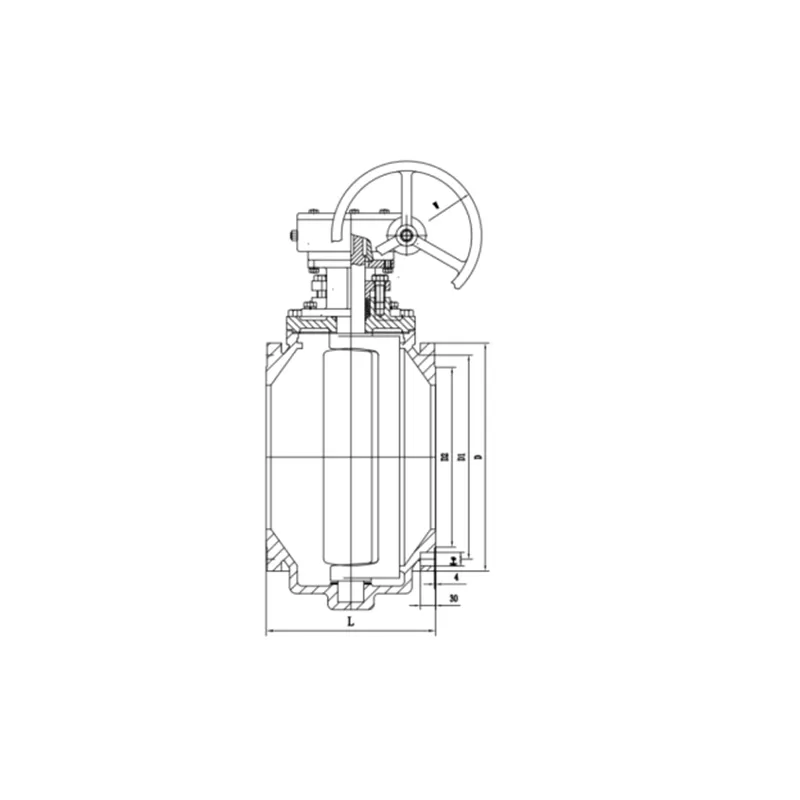
Plug Valve
Plug Valve Purpose
Plug valve is intalled in petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, chemical fertilizer, electric power and other industries in various conditions of the pipeline, used to cut off or connect the pipeline medium.
Plug Valve Definition and Components
What is a Plug Valve and its main parts?
- A Plug Valve is a type of valve that opens or closes the flow passage by rotating an internal plug (or tapered plug). The plug is typically cylindrical or conical with a through port matching the pipeline. It opens when the port aligns with the pipeline and closes with a 90-degree rotation. Its main features are simple structure, low flow resistance, and reliable sealing.
- Main Parts:
- Body: The valve housing that withstands pipeline pressure.
- Plug: The core moving component, usually conical or cylindrical with a through port.
- Stem: Connects the plug to the external actuator, transmitting torque.
- Sealing Assembly: Includes the seal sleeve or rings between the plug and body, and stem packing.
- Actuator: Handwheel, lever, or gear operator.
- End Connections: Flanged, butt-weld, threaded, or socket-weld.
Role, Characteristics, and Application Scenarios of Plug Valve in Pipelines
Functions, Operational Features, Usage Scenarios, and Scenario Diagram
Water Plug Valve Functions: Primarily used for quick shut-off, diversion, or flow direction change in pipelines. Its full-port design results in minimal pressure drop.
Operational Features:
- Quick Operation: Typically requires only a 90-degree turn.
- Bidirectional Seal: Designed to seal from either side.
- Easy Maintenance: Many designs feature top-entry for in-line maintenance.
- Operating Torque: Lubricated plug valves require periodic injection of sealant to reduce friction and wear; non-lubricated types rely on resilient seal materials.
Usage Scenarios:
- Oil & Gas Industry: Wellheads, metering stations, pipelines carrying crude oil or gas with particulates.
- Chemical Industry: Pipelines with slurries, suspended solids, or viscous fluids.
- Wastewater Treatment: Sludge and slurry lines.
- Diversion & Switching: Multi-port plug valves for flow distribution.
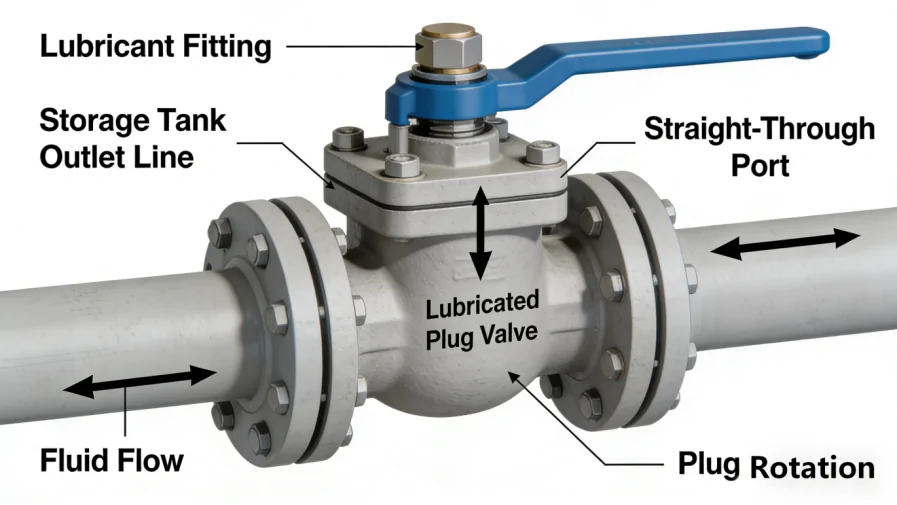
Plug Valve Standards: Materials, Design, and Connections
Material, Design, and Connection Standards
Material Standards:
- Body/Plug: ASTM A216 WCB (Carbon Steel), ASTM A351 CF8/CF8M (Stainless Steel), ASTM A995 4A/5A (Duplex Steel).
- Sealing: Metal seats (Stellite overlayed) or non-metallic seats (PTFE, Reinforced PTFE, Nylon). Lubricated valves use a dedicated sealant system.
Design Standards:
- API 6D (Pipeline Valves) or API 599 (Metal Plug Valves, Flanged, Threaded, and Welding Ends).
- ISO 17292 (Metal ball valves for petroleum, petrochemical and allied industries).
- ASME B16.34 (Valves - Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End).
Connection Standards:
- Flanged Ends: ASME B16.5 or EN 1092-1 (DIN).
- Butt-Weld Ends: ASME B16.25
- Threaded Ends: ASME B1.20.1 (NPT).
How to Select Plug Valve
How to Purchase
- Define Specifications: Determine size, pressure class, operating temperature, media characteristics (presence of solids, corrosiveness, need for fire-safe design). Select type (e.g., lubricated, non-lubricated, multi-port).
- Identify Qualified Suppliers: Select reputable valve manufacturers with API 6D or relevant product certification. Evaluate their experience in similar applications.
- Request Technical Quotation: Provide a detailed inquiry. Request datasheets, material lists, torque curves (for large valves), lubricant system description (if applicable), and dimensional drawings.
- Evaluate and Place Order: Compare technical compliance, price, lead time, and warranty. The purchase order must clearly specify all standards, materials, testing requirements, and document deliverables.
Pre-Shipment Inspection for Export Plug Valve and Key Considerations
Pre-Export Inspection and Precautions
Inspection Protocol:
- Visual & Dimensional Check: Inspect surface finish, markings, flange faces, and key dimensions.
- Material Verification: Cross-check material certificates for major pressure-containing parts.
- Function & Performance Test: Witness Shell Pressure Test and Bidirectional Seat Leakage Test (typically per API 6D or API 598). Test pressures are usually 1.5x working pressure (shell) and 1.1x working pressure (seat).
- Operational Test: Manually operate the valve several times to ensure smooth rotation and accurate position indication. For lubricated valves, check the grease system is clear.
- Coating & Packaging Check: Confirm external coating is intact. Ensure packaging is sturdy to prevent damage and corrosion during transit. Valve ends must have secure protective caps.
Water Valves Precautions:
- Shipping Position: Valve should be partially or fully open to protect sealing surfaces.
- Protect Critical Areas: Flange faces, threads, or weld bevels must be adequately protected.
- Lubricant System: For lubricated valves, ensure grease fittings are sealed and provide spare lubricant in the document pouch.
- Complete Documentation: Ensure each valve has complete documents including Certificate of Conformity, Test Report, Material Certificates, Installation & Maintenance Manual, and Packing List. Exterior packaging must be clearly marked with "Handle with Care," "Keep Dry," contract number, etc.
Plug Valve Main dimensions(mm)
| DN | 15 | 20 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 65 | 80 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 |
| L | 140 | 152 | 165 | 178 | 190 | 216 | 241 | 283 | 305 | 381 | 403 | 419 | 457 | 502 | 762 |
| L1 | 152 | 178 | 203 | 216 | 225 | 267 | 305 | 330 | 356 | 381 | 457 | 521 | 559 | 635 | 762 |
| H | 110 | 115 | 115 | 1135 | 140 | 150 | 165 | 180 | 380 | 460 | 520 | 580 | 620 | 680 | 760 |
| W | 175 | 175 | 175 | 220 | 280 | 305 | 350 | 405 | 300 | 300 | 320 | 320 | 350 | 380 | 450 |
.png)
.png)