ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve
ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve Purpose
Alarm Check Valve is core element in wet pipe fire sprinkler systems. it serves a dual purpose which prevents a reverse flow of water (non-return), also provides for the use of the water motor gong. Meanwhile, in the event of variable pressure condition, false alarm is prevented with provision of retard chamber at the external bypass.
Technical parameters
ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve Main dimensions(mm)
| Model
Strength test |
Working
Pressure(MPa) |
Strength test
Pressure(MPa) |
Strength test Pressure(MPa) | Diametre
(mm) |
Height
(mm) |
Flange
diametre(mm) |
Flange screw hole diametre(mm) | Screw hole specification(mm) |
| ZSFZ80 |
1.6 |
3.2 |
6.4 |
80 | 230 | 200 | 160 | 8*18 |
| ZSFZ100 | 100 | 235 | 220 | 180 | 8*18 | |||
| ZSFZ125 | 125 | 245 | 250 | 210 | 8*18 | |||
| ZSFZ150 | 150 | 250 | 285 | 240 | 8*22 | |||
| ZSFZ200 | 200 | 290 | 340 | 295 | 12*22 | |||
| ZSFZ250 | 250 | 430 | 405 | 355 | 12*26 |
ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve Definition and Components
The ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve is a Chinese fire protection product model code specifically denoting the core control and alarm device for Wet Pipe Automatic Sprinkler Systems.
- Z - Automatic (Zìdòng)
- S - Water Spray (Pēnshuǐ)
- F - Valve (Fámén)
- Z - Alarm (Bàojǐng)
- Therefore, ZSFZ directly translates to "Automatic Water Spray Alarm Valve."
It is a differential-type valve. The system side (piping network) is normally filled with pressurized water. When a sprinkler head activates and discharges water, creating a pressure differential between the upper and lower chambers of the valve, the clapper opens automatically to supply water for extinguishment while simultaneously triggering the hydraulic alarm devices.
Alarm Valve Fire Sprinkler System Main Components:
- Valve Body Assembly: The main housing, containing the inlet, outlet, and valve seat.
- Clapper (Valve Disc): The core opening/closing element. It seals under normal conditions and opens during a fire.
- Retard Chamber: A tank-like device with a small orifice and drain. It filters out transient water flow caused by pressure fluctuations to prevent false alarms, ensuring only sustained water flow (e.g., from sprinkler operation) triggers the alarm.
- Water Motor Gong (Hydraulic Alarm Bell): Water flow drives a turbine, producing a loud mechanical ringing sound for local audible alarm.
- Pressure Switch: Activated by water pressure changes when flow enters the alarm line. It sends an electrical signal to the fire alarm control panel and can automatically start the fire pump.
- Test Valve: Simulates sprinkler operation for periodic functional testing of the valve and alarm devices.
- Drain Valve: Used to drain water from the valve assembly during maintenance.
- Strainer/Filter: Usually installed in the alarm water passage to prevent debris from clogging the retard chamber orifice or damaging the gong
Role, Characteristics, and Application Scenarios of ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve in Pipelines
Fire Sprinkler Alarm Check Valve Functions:
- Automatic Control: Detects sprinkler activation and automatically opens to supply water to the network for firefighting.
- Hydraulic Alarm: Activates the Water Motor Gong for local audible alert.
- Electrical Alarm: Sends an electrical signal via the Pressure Switch to the fire control room.
- System Testing: Provides an interface to test system integrity without activating sprinklers.
Operational Features:
- Differential Principle: Operates based on pressure differential, offering high sensitivity.
- Unidirectional Flow: Allows water flow only from the water supply to the system, preventing backflow.
- Delayed Alarm: Incorporates a retard chamber to effectively prevent false alarms from supply pressure surges.
- Dual Alarm (Mechanical & Electrical): High reliability.
Fire Valves Application Scenarios:
The Wet Alarm Valve is specifically used in Wet Pipe Automatic Sprinkler Systems, suitable for indoor environments where the ambient temperature is consistently above 4°C (39°F) and below 70°C (158°F). This is the most widely used automatic sprinkler system globally.
- Office buildings, hotels, hospitals, schools
- Shopping malls, retail centers
- Libraries, museums
- Light industrial facilities
- Common areas of residential buildings
Scenario Diagram:
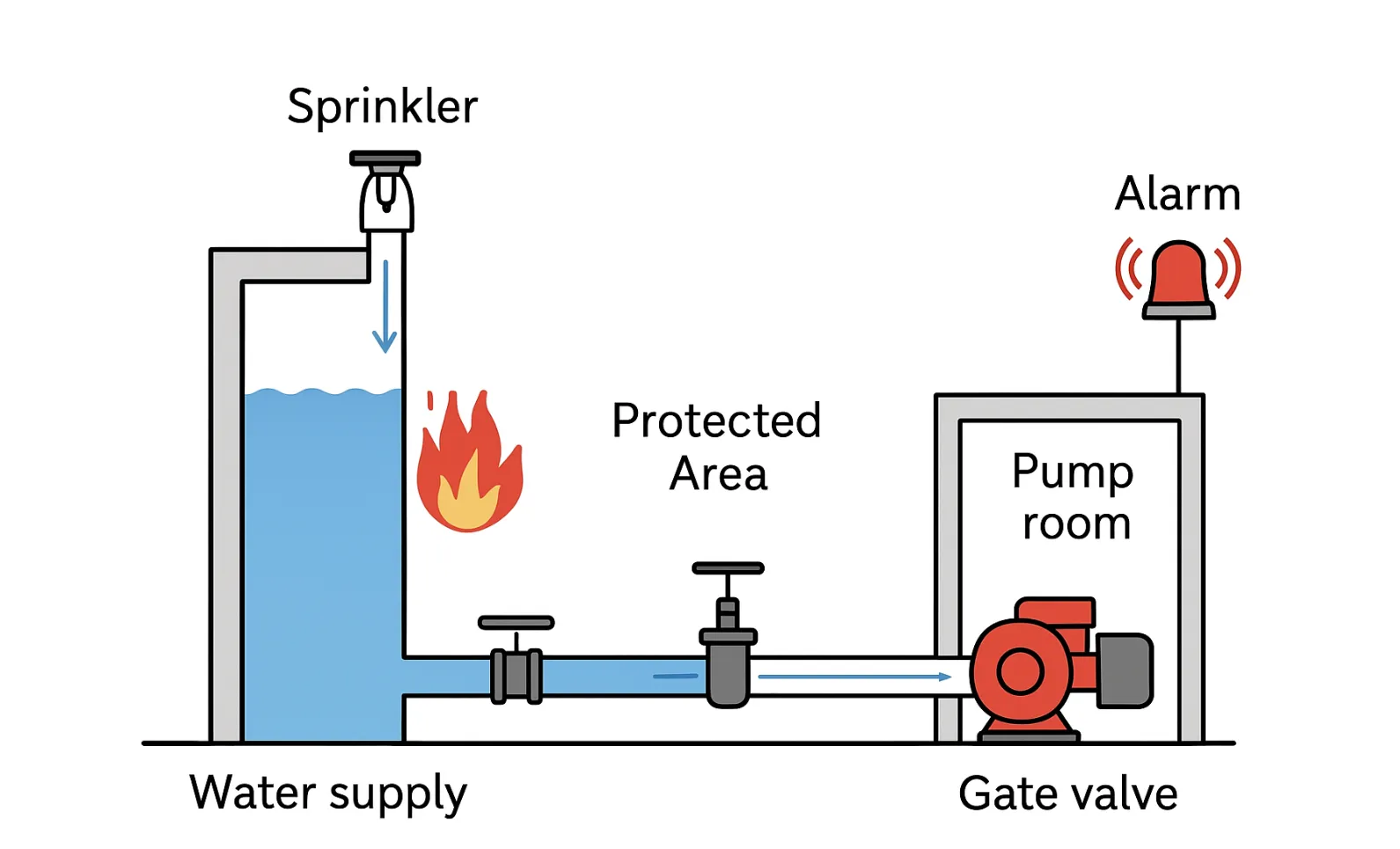
ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve Standards: Materials, Design, and Connections
Ensure the valve complies with the following key standards during procurement:
Design & Performance Standards:
- GB 5135.2-2019: "Automatic fire sprinkler systems — Part 2: Wet alarm valves, retard chambers and water motor alarms" — This is the Chinese Mandatory National Product Standard and the fundamental basis for product design and performance testing.
- UL 193: Underwriters Laboratories Standard (USA).
- FM Global Approval: FM Approvals standard (USA).
- EN 12259-1: European Standard.
Material Standards:
- Body & Bonnet: Typically made of Ductile Iron (e.g., QT450-10) per GB/T 1348. Also available in copper alloy, stainless steel, etc.
- Internals: Critical sealing components like the clapper and seat are often made of copper alloy, stainless steel, or corrosion-resistant composites.
- Spring: Stainless steel.
- Coatings: Internal and external body coatings (e.g., epoxy resin) for hygiene and corrosion protection.
Connection Standards:
- Flanged Connection: Most common. Specify the flange standard (e.g., GB/T 9113 Chinese National, ANSI B16.1 American, EN 1092-2 European) and pressure class (e.g., PN16/Class 125).
- Threaded Connection: For smaller diameter valves.
- Crucial Purchase Info: Always provide connection type, standard, Nominal Diameter (DN), and Pressure Rating (PN/Class).
How to Select ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve
①Define Technical Specifications:
- Nominal Diameter (DN50, DN65, DN80, DN100, DN150, etc.).
- Working Pressure Rating (e.g., PN16).
- Connection Standard (Flange type, bolt hole circle, thickness).
- Required Certifications (e.g., CCCF (China), UL, FM, CE).
- Operating Environment (Standard / Special corrosive conditions).
②Source Qualified Suppliers:
- Prioritize manufacturers holding valid "China Compulsory Certification for Fire Products (CCCF)". This is a legal requirement for sale and installation in China.
- Find manufacturers via industry trade shows (e.g., China International Fire Safety Expo), B2B platforms (Alibaba), or industry association referrals.
- Evaluate the supplier's qualifications, production scale, quality control system, and export experience.
③Request Quotations & Negotiate:
- Provide detailed technical specs. Request product catalogs, certification copies, and material reports.
- Clarify if pricing includes tax, packaging, and shipping to port (Trade terms: FOB, CIF, etc.).
- Confirm Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ), lead time, and payment terms.
④Sign the Contract:
- The contract should clearly list all technical specifications, standards, certification requirements, packaging, delivery schedule, inspection methods, and warranty terms.
- Emphasize that products must be new, unused, and conform to agreed standards.
⑤Arrange Production & Inspection:
Consider arranging Third-Party Inspection (TPI) during production and upon completion
Pre-Shipment Inspection for Export ZSFZ Wet Alarm Valve and Key Considerations
Inspection Procedure (Recommended to be performed by a professional QC or third-party agency):
- Document Review:
Verify product certificates, material certificates, and factory test reports.
Cross-check the CCCF certification documents with the physical "Fire Product Identity Information Mark (S-Mark)" on the valve.
Check the packing list against the actual quantity and model numbers.
- Visual & Dimensional Inspection:
Inspect the valve body casting for smoothness, defects like sand holes, or cracks.
Check coatings for uniformity and absence of peeling.
Use calipers to sample critical connection dimensions (flange OD, thickness, bolt hole center distance).
Verify the information on the nameplate (Model, DN, PN, Manufacturer, Date) is clear and correct.
- Functional Testing:
Leakage Test: Block the valve outlet, apply rated working pressure to the inlet, and check the clapper seal for any leakage.
Alarm Function Test: Slowly open the test valve, observe and record:
Whether the retard chamber fills and triggers the Water Motor Gong within 5 to 90 seconds(sound intensity must meet standards).
Whether the pressure switch activates and outputs the correct electrical signal.
Reset Test: Close the test valve. Confirm the alarm stops and the retard chamber drains and resets automatically.
- Packaging Inspection:
Check for export wooden crates (must comply with ISPM 15 phytosanitary standard with a clear IPPC mark).
Internal packaging should have moisture-proof material (e.g., plastic bags, anti-rust paper). Components must be securely fastened to prevent damage during transit.
Shipping marks on the crate (Consignee, Product Name, Model, Case No., Gross Weight, Dimensions, "Fragile," "This Side Up") must be clear and accurate.
Key Precautions:
- Certification Compliance: Products without valid CCCF certification cannot be legally used in China and pose a significant risk in export transactions.
- Test Water Quality: Use clean water for testing to prevent valve clogging.
- Post-Test Drying: After all functional tests, completely drain all water from the valve and piping. Use compressed air to dry the interior thoroughly, especially the retard chamber and gong, to prevent internal rust or freezing damage during sea transit.
- Complete Accessories: Ensure all bolts, gaskets, special tools, and manuals are included.
- Record Keeping: Take photos of key testing processes and final packaging as evidence.
.png)
.png)





